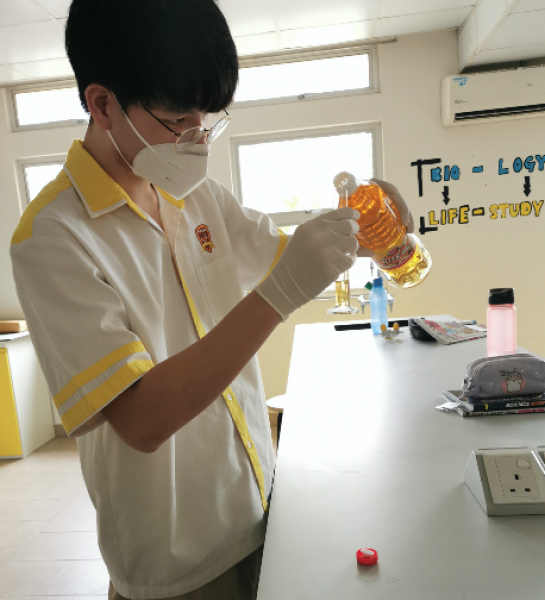
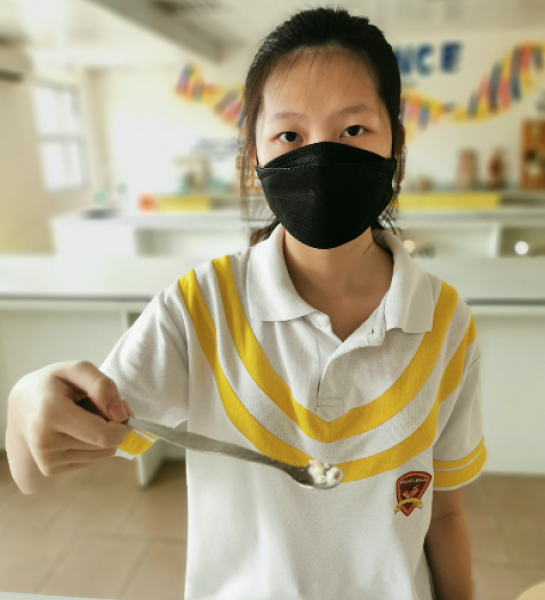
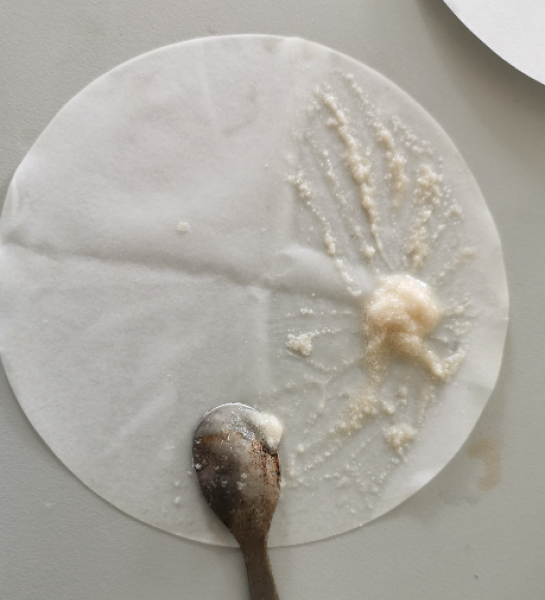
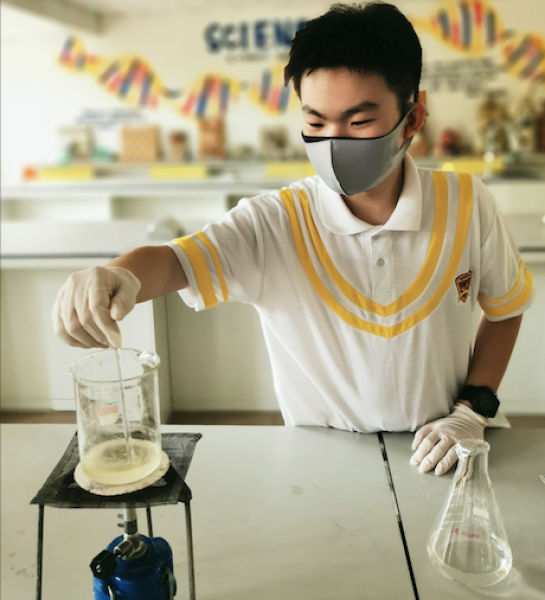
Form 5 students conducted an experiment on saponification, a process that involves the conversion of fat, oil, or lipid, into soap and alcohol by the action of aqueous alkali (e.g. NaOH).
Soaps are salts of fatty acids, which in turn are carboxylic acids with long carbon chains. A typical soap is sodium oleate.
Palm oil was used in this experiment.